Examining the frequency of dysphagia and the predictive factors of dysphagia that require attention in patients with Parkinson's disease
- Authors: Babajani Roshan T.1, Behzad C.1, Saadat P.1, Bijani A.1, Dehghan M.1, Ahmadi Ahangar A.1
-
Affiliations:
- Babol University of Medical Sciences
- Issue: Vol 17, No 1 (2023)
- Pages: 14-19
- Section: Original articles
- Submitted: 01.08.2022
- Accepted: 14.11.2022
- Published: 29.03.2023
- URL: https://www.annaly-nevrologii.com/journal/pathID/article/view/874
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.54101/ACEN.2023.1.2
- ID: 874
Cite item
Full Text
Abstract
Introduction. Due to the prevalence of dysphagia in patients with Parkinson's disease (PD) and its complications such as aspiration pneumonia, which is the main cause of death in these patients, PD-related disability can be prevented by early diagnosis and treatment of dysphagia.
Objective. The present study was aimed at investigating the frequency of dysphagia in PD patients.
Materials and methods. This cross-sectional study included 150 PD patients visiting a Neurology Clinic. The severity of PD was determined based on the Unified Parkinson Disease Rating Scale (UPDRS) and modified Hoen and Yahr (HYS) Scale. The Munich Dysphagia Test-Parkinson's disease (MDT-PD) questionnaire was used to assess dysphagia. Comparisons were made using generalized Fisher exact, Chi-square, ANOVA, and Kruskal–Wallis tests. Predictive factors were analyzed using logistic regression. Statistical analyses were performed at significance level of 0.05.
Results. Out of all 150 patients referred to the Clinic, the prevalence of dysphagia requiring attention was 25.3% (n = 38). The patients of the three groups according to the MDT-PD (no noticeable dysphagia, noticeable oropharyngeal, and dysphagia with aspiration risk) had a significant difference only in terms of the PD duration (p < 0.001). In the predicting of dysphagia, the longer PD duration (p = 0.011) and homemaker occupation (p = 0.033) were protective factors, while female gender was a risk factor (p = 0.011).
Conclusion. The prevalence of dysphagia requiring attention in the studied patients was 25.3%. It decreased with the longer duration of the disease, and its prevalence was lower in homemaker patients, while the odds of dysphagia was 5.8 times higher in women than in men.
Keywords
Full Text
Introduction
Parkinson's disease (PD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder associated with the loss of dopaminergic neurons in the pars compacta of the substantia nigra [1]. PD is the second most common neurodegenerative disorder after Alzheimer's disease [2].
Various studies describe PD as a disease that affects the whole body and suggest that its source is the intestines before affecting the brainstem, often leading to gastrointestinal disorders in the early stage of the disease [3]. PD as a neurological disorder that can affect the efficiency of the swallowing function with increased muscle tone, involuntary movements, and lack of coordination between movements resulting in dysphagia [4]. Although little is known about the pathophysiology of dysphagia in patients with PD, it seems that dopaminergic and non-dopaminergic mechanisms are involved in the development of dysphagia in these patients [3].
More than 80% of patients with PD develop dysphagia during their life. In developed countries, the prevalence of dysphagia in patients over 60 years is 0.3 to 1% and 3% in patients over 80 years [5, 6]. Dysphagia in PD is associated with significant clinical complications such as malnutrition, drug consuming problems, dehydration, and aspiration pneumonia that is the main cause of death in patients with PD. One of the reasons mentioned for unrecognized dysphagia in these patients is the lack of attention to swallowing function during neurological examination [3].
Various methods can detect dysphagia in patients with PD, for example, fiberoptic endoscopy, videofluoroscopy, and high-resolution manometry [3]. But the first step is a proper questionnaire. One of the standard questionnaires for PD is the Munich Dysphagia Test- Parkinson's disease (MDT-PD) with a sensitivity of 82.4% and a specificity of 61.9% [7]. MDT-PD identifies even mild oropharyngeal dysphagia with and without risk of aspiration in patients with PD [3]. Studies showed that early treatment of dysphagia can provide safer feeding for patients with PD in the long-term perspective [4]. However, the effect of dopaminergic drugs, especially levodopa, on swallowing function and their role in the treatment of dysphagia is controversial [8–10]. Some studies showed significant improvement in dysphagia after using dopaminergic drugs in some patients with PD [7–22].
Concerning the prevalence of dysphagia in patients with PD, which was reported to be as high as 80%, as well as its complications such as aspiration pneumonia that is the most important cause of death in these patients, early diagnosis and treatment of dysphagia are important [3]. Therefore, the current study was aimed to evaluate the frequency of dysphagia in patients with PD using the MDT-PD.
Materials and methods
Population of patients
This cross-sectional analytic study included 150 patients with a clinically confirmed diagnosis of Idiopathic PD based on classic symptoms of the disease (tremor, bradykinesia, rigidity and postural instability). The patients were referred to Rouhani Teaching Hospital in Babol from March 2018 to February 2020 [1].
The exclusion criteria were neuroleptic-induced Parkinson's syndromes and a history of other diseases that affected swallowing function such as stroke or gastrointestinal diseases leading to dysphagia. Also, patients with severe mental disorders or dementia were excluded. This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Babol University of Medical Sciences under the code of MUBABOL.REC.1399.205. All individuals signed written informed consent.
In order to determine the severity of PD, the scoring systems of the Unified Parkinson Disease Rating Scale (UPDRS) [23] and the modified Hoen and Yahr Scale (HYS) [24] were used.
UPDRS includes the following parts:
1) mind, behavior and mood (4 questions);
2) activities of daily living (13 questions);
3) motor examination (14 questions);
4) complications of therapy (11 questions).
HYS consists of 8 stages according to motor severity of PD. It includes scores from zero (no signs of disease) to five (wheelchair bound or bedridden unless aided) [25]. In both scales, a higher score indicates more disability. Definite diagnosis of PD and its varying stages was made by one neurologist.
MDT-PD was used to determine dysphagia in patients with PD. The Persian version of MDT-PD was found to be reliable (Cronbach's alpha: 0.897) and valid based on the viewpoint of five neurologists. The MDT-PD questionnaire consists of 26 questions presented in 4 sections:
1) difficulty swallowing food and liquids;
2) difficulty swallowing independent from food intake;
3) further swallowing-specific and accompanying burden;
4) swallowing-specific health questions.
This questionnaire is available online at www.mdt-parkinson.de. By completing it, patients can be classified into the following three groups: no noticeable dysphagia, noticeable oropharyngeal dysphagia, and dysphagia with aspiration risk. Data such as PD duration and demographic information including age, sex, body mass index (BMI), occupation (employed, unemployed, homemaker), educational level (illiterate, middle school, diploma, upper diploma), marital status (married, unmarried), residency (urban, rural) and smoking (yes/no) were collected from the patients.
Statistical analysis
The categorical variables were described by frequency (percentage), whereas continuous variables were described by the mean (± SD). The generalized Fisher exact test and Chi-square test (for categorical variables) and ANOVA and Kruskal–Wallis tests (for continuous variables) were used to compare characteristics between the patients with no noticeable dysphagia, noticeable oropharyngeal, and dysphagia with aspiration risk.
By merging two groups of patients with noticeable oropharyngeal dysphagia and dysphagia with aspiration risk, as dysphagia requiring attention, predictive factors were analyzed using logistic regression. The regression model was fitted using the backward stepwise; odds ratio (OR) and confidence interval (CI) were reported. Statistical analyses were carried out with SPSS v. 22.0. The level of statistical significance was set at α = 0.05 for all ana- lyses.
Results
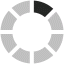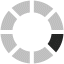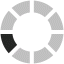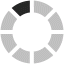
Patients with no noticeable dysphagia, noticeable dysphagia and dysphagia with aspiration risk were compared in terms of research variables. The results are presented in Table 1. Among 150 patients with PD, 84 (56%) were male and 66 (44%) were female with the mean ± Standard Deviation (SD) age of 70.07 ± 9.38 years. Based on the results of MDT-PD (Table 2), 112 patients (74.67%) had no noticeable dysphagia, 14 patients (9.33%) had noticeable dysphagia and 24 patients (16.00%) had dysphagia with aspiration risk. In total, this study reported that 38 patients (25.33%) had dysphagia requiring attention. The Fi-gure represents the frequency of PD severity based on HYS.
Distribution of PD severity based on HYS stage.
Table 1. Comparison of descriptive indices of research variables in patients with no noticeable dysphagia, significant oropharyngeal dysphagia and dysphagia with aspiration risk
Variables | Total | Dysphagia | Statistics | р-value | |||
no noticeable dysphagia | noticeable oropharyngeal dysphagia | dysphagia with aspiration risk | |||||
Demographic variables and smoking status | |||||||
Age | 70.07 ± 9.38 | 70.48 ± 9.16 | 72.07 ± 9.81 | 67.00 ± 9.88 | 1.726a | 0.182 | |
BMI | 25.97 ± 4.55 | 25.60 ± 4.71 | 27.52 ± 4.62 | 26.79 ± 3.49 | 1.985b | 0.159 | |
Gender | male | 84 (56.00) | 64 (76.19) | 7 (8.33) | 13 (15.48) | 0.297c | 0.862 |
female | 66 (32.00) | 48 (72.73) | 7 (10.60) | 11 (16.67) | |||
Education | illiterate | 78 (52.00) | 57 (73.08) | 11 (14.10) | 10 (12.82) | 8.487d | 0.075 |
middle school | 48 (32.00) | 35 (72.92) | 1 (2.08) | 12 (25.00) | |||
diploma and upper | 23 (15.33) | 19 (82.60) | 2 (8.70) | 2 (8.70) | |||
unkown | 1 (0.67) | – | – | – | |||
Occupation | unemployed | 42 (28.00) | 30 (71.42) | 6 (14.29) | 6 (14.29) | 2.846d | 0.584 |
homemaker | 54 (36.00) | 43 (79.63) | 4 (7.41) | 7 (12.96) | |||
employed | 54 (36.00) | 39 (72.22) | 4 (7.41) | 11 (20.37) | |||
Marriage status | single | 32 (21.33) | 21 (65.62) | 3 (9.38) | 8 (25.00) | 2.505d | 0.286 |
married | 118 (78.67) | 91 (77.12) | 11 (9.32) | 16 (13.56) | |||
Residency | rural | 77 (51.33) | 61 (79.22) | 5 (6.49) | 11 (14.29) | 2.097c | 0.350 |
urban | 73 (48.67) | 51 (69.86) | 9 (12.33) | 13 (17.81) | |||
Smoking | no | 143 (95.33) | 109 (76.22) | 13 (9.09) | 21 (14.69) | 4.498d | 0.105 |
yes | 7 (4.67) | 3 (42.86) | 1 (14.28) | 3 (42.86) | |||
Disease related and clinical variables | |||||||
PD duration (months) | 69.39 ± 56.85 | 76.82 ± 59.81 | 32.43 ± 37.57 | 56.25 ± 39.94 | 12.600b | < 0.001 | |
Severity based on UPDRS | 52.43 ± 25.72 | 50.59 ± 24.83 | 63.79 ± 34.88 | 54.38 ± 22.86 | 1.486b | 0.223 | |
Severity based on HYS | stage 1 | 4 (2.67) | 3 (75.00) | 1 (25.00) | – | 10.417d | 0.579 |
stage 1.5 | 19 (12.67) | 14 (73.68) | 2 (10.53) | 3 (15.79) | |||
stage 2 | 43 (28.67) | 35 (81.40) | 4 (9.30) | 4 (9.30) | |||
stage 2.5 | 28 (18.67) | 22 (78.57) | 1 (3.57) | 5 (17.86) | |||
stage 3 | 37 (24.67) | 25 (67.57) | 3 (8.11) | 9 (24.32) | |||
stage 4 | 17 (11.33) | 12 (70.59) | 2 (11.77) | 3 (17.65) | |||
stage 5 | 2 (1.33) | 1 (50.00) | 1 (50.00) | – | |||
Tremor | no | 13 (8.67) | 10 (76.92) | – | 3 (23.08) | 1.784d | 0.410 |
yes | 137 (91.33) | 102 (74.45) | 14 (10.22) | 21 (15.33) | |||
Bradykinesia | no | 14 (9.33) | 11 (78.57) | 1 (7.14) | 2 (14.29) | 0.139d | 0.933 |
yes | 136 (90.67) | 101 (74.26) | 13 (9.56) | 22 (16.18) | |||
Rigidity | no | 19 (12.67) | 14 (73.68) | 3 (15.79) | 2 (10.53) | 1.382d | 0.501 |
yes | 131 (87.33) | 98 (74.81) | 11 (8.40) | 22 (16.79) | |||
Postural instability | no | 67 (44.67) | 54 (80.59) | 6 (8.96) | 7 (10.45) | 2.922c | 0.232 |
yes | 83 (55.33) | 58 (69.88) | 8 (9.64) | 17 (20.48) | |||
Note. For quantitative variables; mean (± SD) and qualitative variables; frequency (%). aANOVA test; bKruskal–Wallis test; cChi-square test; dGeneralized Fisher exact test.
The results from Table 1 show that the patients under investigation in the three groups no noticeable dysphagia, oropharyngeal dysphagia and dysphagia with aspiration risk had a signifi- cant difference only in terms of Parkinson's disease duration (p < 0.001).
After merging two groups (noticeable oropharyngeal dysphagia and dysphagia with aspiration risk) as dysphagia requiring attention (Table 2), in order to find predictive factors for dysphagia, the multivariate logistic regression with backward method was used. The results (the final step) are presented in the Table 3.
Table 2. The frequency of dysphagia requiring attention in PD patients
Group | Frequency, % | |
No noticeable dysphagia | 112 (74.67) | |
Dysphagia requiring attention Total = 38 (25.33) | noticeable oropharyngeal dysphagia | 14 (9.33) |
dysphagia with aspiration risk | 24 (16.00) | |
Table 3. Final step of the multivariate logistic regression analysis (backward selection) to investigate the factors that predict dysphagia requiring attention (noticeable oropharyngeal dysphagia and dysphagia with aspiration risk)
Variables | Odds ratio (CI 95%) | р-value | |
Gender | male (reference) | ||
female | 5.863 (1.496–22.972) | 0.011 | |
Occupation | unemployed (reference) | ||
homemaker | 0.202 (0.047–0.879) | 0.033 | |
employed | 1.025 (0.381–2.760) | 0.960 | |
Smoking | no (reference) | ||
yes | 4.408 (0.861–22.556) | 0.075 | |
PD duration | 0.987 (0.977–0.997) | 0.011 | |
As shown, the longer PD duration (p = 0.011) and homemaker occupation (p = 0.033) are protective factors for dysphagia. In other words, with the longer PD duration, the possibility of dysphagia requiring attention decreases (OR = 0.987) and the possibility of dysphagia for homemaker patients is lower (OR = 0.202).
Female gender has been a risk factor for the occurrence of dysphagia that needs attention (p = 0.011); the chance of dysphagia requiring attention for women is estimated to be 5.863 folds higher that in male.
Discussion
The study showed that the frequency of dysphagia requiring attention in patients with PD was 25.33%. A few studies were found using the MDT-PD to determine dysphagia in patients with PD. Based on a meta-analysis study, the prevalence of dysphagia according to PD patients' self-reports varied from 16% to 55%, and when dysphagia was diagnosed by objective assessments, its prevalence was 72% to 87%. The above study stated that oropharyngeal dysphagia develops in at least one third of patients with PD, which depends on the severity of the disease and the assessment technique [26]. Е. Michou and colleagues found that the prevalence of swallowing disorders in patients with PD by using Swallowing disturbance questionnaire (SDQ) was 50% [27]. Therefore, the low prevalence of dysphagia in the present study could be attributed to the fact that the information obtained in the MDT-PD was based on the patients' reports.
It was concluded that the patients under investigation in three groups of no noticeable dysphagia, oropharyngeal dysphagia and dysphagia with aspiration risk had a significant difference only in terms of the duration of their disease. According to X. Ding and colleagues' study, there was no significant difference in PD duration in patients with or without dysphagia [28], whereas Е. Cereda and colleagues showed that PD duration and dementia were associated with swallowing disorders in PD patients [29].
In the study of K. Lam and colleagues, BMI in patients with PD who had dysphagia was significantly lower than patients without dysphagia [12], while in our study the difference of BMI was not significant.
A. Galib and colleagues demonstrated that the disease severity and PD duration were not predictors of dysphagia in these patients. According to their study, although patients with dysphagia had a shorter time from diagnosis, but this association was not statistically significant [30].
According to the results of the regression model fitted in this study, the longer PD duration was a protective factor for dysphagia. In order to justify this relationship, it could be said that patients with longer PD duration might have benefit in terms of dose adjustment rather than patients who had recently been diagnosed. Evidence showed that levodopa has a good effect on the swallowing function as well as motor symptoms in limbs [31].
T. Warnecke and colleagues found that increasing the daily dose of levodopa could be effective for 50% of patients with oropharyngeal dysphagia and motor fluctuations. According to the same study, dopaminergic stimulation of the central nervous system is highly associated with the earlier onset of the swallowing reflex, which is very effective in clearing the pharynx [32].
One of the major strengths of our study is that we included PD patients with all HYS stages. Based on the current study, stage 2 and 3 of PD were most frequent, 28.7% and 24.7% respectively. Interestingly, PD severity based on HYS was not associated with dysphagia. X. Ding and colleagues found that patients at more severe stages were 3.26 times more likely to develop dysphagia [28]. In the present study, a few patients were at stages of 4 and 5, which might explain the lack of association between disease severity and dysphagia.
In this study, among the demographic variables, the effect of gender and housework were significant in predicting dysphagia. But according to X. Ding and colleagues 's study, there was no significant difference between gender in patients with or without dysphagia [28], whereas Cereda and colleagues showed that age and gender were associated with swallowing disorders in PD patients [29].
Also, the homemaker occupation was effective as a protective factor. As a result, it could be said that householders are less likely to have oropharyngeal dysphagia or dysphagia with aspiration risk. Of course, to prove this claim more detailed studies are required.
The limitations of this study included inability of patients with higher stages to arrive at hospital and not considering the effects of patient's lifestyle, dental hygiene and the on-off status of PD. Further large-scale studies are needed to evaluate the prevalence of dysphagia in patients with PD considering these limitations.
Conclusion
This study reported that the prevalence of dysphagia in patients with PD was relatively low being about 25%. The mean PD duration in patients with no noticeable dysphagia was longer than in patients with dysphagia requiring attention. The longer PD duration and homemaker occupation were protective factors and female gender was a risk factor of dysphagia.
Findings of this study can help neurologists to detect swallowing disorders in patients with PD at the mild stage, so that it can be treated earlier. In this way, the progression of dysphagia and its complications can be prevented and the quality of life can be improved.
Author contribution. Payam Saadat — concept and design. Ali Bijani — analysis and interpretation of the results. Payam Saadat, Tahereh Babajani Roshan, Catherine Behzad, Ali Bijani and Alijan Ahmadi-Ahangar — data collection, writing of the draft. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Ethics approval. The study was conducted after obtaining informed consent from the patients.
Acknowledgement. The authors would like to thank the Deputy for Research and Technology of Babol University of Medical Sciences and Rouhani Hospital Clinical Research Development Unit for their support.
Source of funding. This study was not supported by any external sources of funding.
Conflict of interest. The authors declare no apparent or potential conflicts of interest related to the publication of this article.
About the authors
Tahereh Babajani Roshan
Babol University of Medical Sciences
Email: t.doctor_91@yahoo.com
Medical Student, Student Research Committee
Iran, Islamic Republic of, Babol, MazandaranCatherine Behzad
Babol University of Medical Sciences
Email: catherinebehzad@yahoo.com
Assistant Professor, Gastroenterology and Hepatology Department of Internal Medicine
Iran, Islamic Republic of, Babol, MazandaranPayam Saadat
Babol University of Medical Sciences
Author for correspondence.
Email: sepanta1968@yahoo.com
Associated Professor, Mobility Impairment Research Center
Iran, Islamic Republic of, Babol, MazandaranAli Bijani
Babol University of Medical Sciences
Email: alibijani@yahoo.com
Assistant Professor, Epidemiology, Health Research Institute
Iran, Islamic Republic of, Babol, MazandaranMehdi Dehghan
Babol University of Medical Sciences
Email: m.dehghan26@gmail.com
Master of Science of Speech and Language Pathology
Iran, Islamic Republic of, Babol, MazandaranAlijan Ahmadi Ahangar
Babol University of Medical Sciences
Email: rohanresearch88@gmail.com
Professor, Neurology, Mobility Impairment Research Center
Iran, Islamic Republic of, Babol, MazandaranReferences
- Çamcı G., Oğuz S. Association between Parkinson’s disease and Helicobacter pylori. J. Clin. Neurol. 2016; 12(2): 147–150. doi: 10.3988/jcn.2016.12.2.147
- Pringsheim T., Jette N., Frolkis A., Steeves T.D. The prevalence of Parkinson’s disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Mov. Disord. 2014; 29(13): 1583–1590. doi: 10.1002/mds.25945
- Suttrup I., Warnecke T. Dysphagia in Parkinson’s disease. Dysphagia. 2016; 31(1): 24–32. doi: 10.1007/s00455-015-9671-9
- Luchesi K.F., De Toledo I.P., Mourao L.F. Dysphagia in Parkinson’s disease: prevalence, impact and management challenges. J. Otolaryngol. ENT Res. 2017; 6(5): 00176. doi: 10.15406/joentr.2017.06.00176
- López-Liria R., Parra-Egeda J., Vega-Ramírez F.A. et al. Treatment of dysphagia in Parkinson’s disease: a systematic review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 2020; 17(11): 4104. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17114104
- Benito-Leon J. Epidemiology of Parkinson’s disease in Spain and its contextualisation in the world. Rev. Neurol. 2018; 66(4): 125–134.
- Simons J.A., Fietzek U.M., Waldmann A. et al. Development and validation of a new screening questionnaire for dysphagia in early stages of Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2014; 20(9): 992–998. doi: 10.1016/j.parkreldis.2014.06.008
- Sutton J.P. Dysphagia in Parkinson’s disease is responsive to levodopa. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2013; 19(3): 282–284. doi: 10.1016/j.parkreldis.2012.11.007
- Chaudhuri K.R., Healy D.G., Schapira A.H. Non-motor symptoms of Parkinson’s disease: diagnosis and management. Lancet Neurol. 2006; 5(3): 235–245. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(06)70373-8
- Jankovic J. Parkinson’s disease: clinical features and diagnosis. J. Neurol Neurosurg. Psychiatry. 2008; 79(4): 368–376. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.2007.131045
- Warnecke T., Hamacher C., Oelenberg S., Dziewas R. Off and on state assessment of swallowing function in Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2014; 20(9): 1033–1034. doi: 10.1016/j.parkreldis.2014.06.016
- Lam K., Lam F.K., Lau K.K. et al. Simple clinical tests may predict severe oropharyngeal dysphagia in Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2007; 22(5): 640–644. doi: 10.1002/mds.21362
- Manor Y., Giladi N., Cohen A. et al. Validation of a swallowing disturbance questionnaire for detecting dysphagia in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2007; 22(13): 1917–1921. doi: 10.1002/mds.21625
- Prosiegel M. Neurogene dysphagien. Nervenarzt. 2007; 78(10): 1209–1217. doi: 10.1055/s-0038-1629949
- Heijnen B.J., Speyer R., Baijens L.W., Bogaardt H.C. Neuromuscular electrical stimulation versus traditional therapy in patients with Parkinson’s disease and oropharyngeal dysphagia: effects on quality of life. Dysphagia. 2012; 27(3): 336–345. doi: 10.1007/s00455-011-9371-z
- Manor Y., Mootanah R., Freud D. et al. Video-assisted swallowing therapy for patients with Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2013; 19(2): 207–211. doi: 10.1016/j.parkreldis.2012.10.004
- Athukorala R.P., Jones R.D., Sella O., Huckabee M.L. Skill training for swallowing rehabilitation in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2014; 95(7): 1374–1382. doi: 10.1016/j.apmr.2014.03.001
- Luchesi K.F., Kitamura S., Mourão L.F. Dysphagia progression and swallowing management in Parkinson’s disease: an observational study. Braz. J. Otorhinolaryngol. 2015; 81(1): 24–30. doi: 10.1016/j.bjorl.2014.09.006
- Langmore S.E. Evaluation of oropharyngeal dysphagia: which diagnostic tool is superior? Curr. Opin. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2003; 11(6): 485–489. doi: 10.1097/00020840-200312000-00014
- Suttrup I., Oelenberg S., Hamacher C. et al. Endoscopic L-dopa-test for parkinsonian dysphagia (a pilot study). Dysphagia. 2011; 26: 482.
- Lim A., Leow L., Huckabee M.L. et al. A pilot study of respiration and swallowing integration in Parkinson’s disease: “on” and “off” levodopa. Dysphagia. 2008; 23(1): 76–81. doi: 10.1007/s00455-007-9100-9
- Hirano M., Isono C., Sakamoto H. et al. Rotigotine transdermal patch improves swallowing in dysphagic patients with Parkinson’s disease. Dysphagia. 2015; 30(4): 452–456. doi: 10.1007/s00455-015-9622-5
- Goetz C.G., Tilley B.C., Shaftman S.R. et al. Movement disorder society-sponsored revision of the Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale (MDS-UPDRS): scale presentation and clinimetric testing results. Mov. Disord. 2008; 23(15): 2129–2170. doi: 10.1002/mds.22340
- Goetz C.G., Poewe W., Rascol O. et al. Movement Disorder Society Task Force report on the Hoehn and Yahr staging scale: status and recommendations the Movement Disorder Society Task Force on rating scales for Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2004; 19(9): 1020–1028. doi: 10.1002/mds.20213
- Zamani P. Prevalence of dysphagia in patients admitted to Ahvaz teaching hospitals in the first six months of 2010. J. Med. Life. 2012; 11(3): 261–268.
- Kalf J.G., de Swart B.J., Bloem B.R., Munneke M. Prevalence of oropharyngeal dysphagia in Parkinson’s disease: a meta-analysis. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2012; 18(4): 311–315. doi: 10.1016/j.parkreldis.2011.11.006
- Michou E., Hamdy S., Harris M. et al. Characterization of corticobulbar pharyngeal neurophysiology in dysphagic patients with Parkinson’s disease. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014; 12(12): 2037–2045. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2014.03.020
- Ding X., Gao J., Xie C. et al. Prevalence and clinical correlation of dysphagia in Parkinson disease: a study on Chinese patients. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2018; 72(1): 82–86. doi: 10.1038/ejcn.2017.100
- Cereda E., Cilia R., Klersy C. et al. Swallowing disturbances in Parkinson’s disease: a multivariate analysis of contributing factors. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2014; 20(12): 1382–1387. doi: 10.1016/j.parkreldis.2014.09.031
- Ali G., Wallace K.L., Schwartz R. et al. Mechanisms of oral-pharyngeal dysphagia in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Gastroenterology. 1996; 110(2): 383–392. doi: 10.1053/gast.1996.v110.pm8566584
- Logemann J. Evaluation and treatment of swallowing disorders. 2nd ed. Austin, Tex; 1998. P. 456–970.
- Buhmann C., Flügel T., Bihler M. et al. Is the Munich dysphagia Test–Parkinson’s disease (MDT-PD) a valid screening tool for patients at risk for aspiration? Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2019; 61: 138–143. doi: 10.1016/j.parkreldis.2018.10.031
- Tiple D., Fabbrini G., Colosimo C. et al. Camptocormia in Parkinson disease: an epidemiological and clinical study. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry. 2009; 80(2): 145–148. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.2008.150011
Supplementary files